Data recovery tools are essential in retrieving lost, deleted, or inaccessible data from various storage devices, such as hard drives, SSDs, USB drives, and memory cards. These tools come in different forms, including software-based solutions, hardware-based devices, and specialized forensic tools. Each type of tool offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to select the right tool based on the specific recovery scenario. Software-based recovery tools are among the most widely used due to their accessibility and ease of use. These tools typically offer user-friendly interfaces that allow individuals to recover data without requiring deep technical expertise. They can recover data from logically damaged drives, such as those with corrupted file systems, deleted files, or formatted partitions. However, software-based tools have limitations, particularly when dealing with physically damaged drives or encrypted data, as they rely on the underlying hardware being functional and accessible.
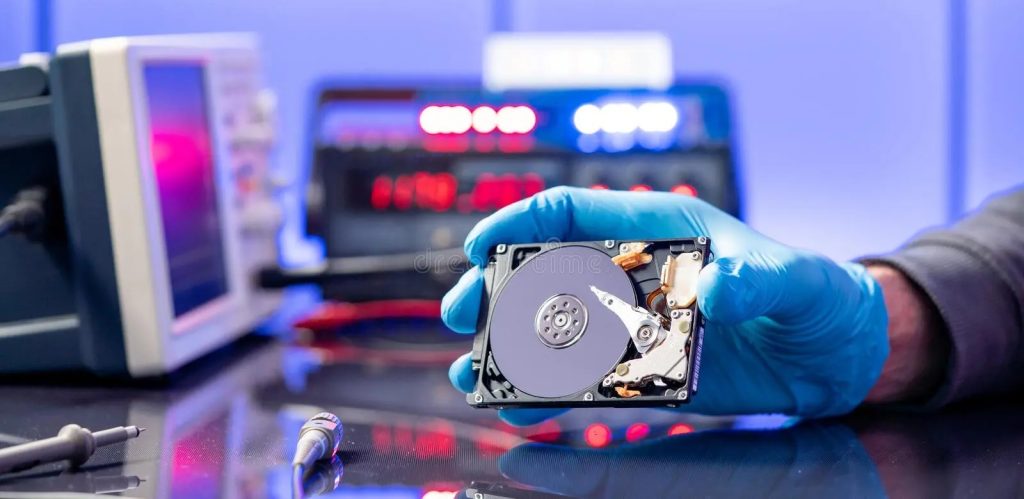
Hardware-based recovery tools are designed to address more complex recovery scenarios, such as drives with physical damage, firmware corruption, or issues with drive controllers. These tools often include disk duplicators, write blockers, and specialized recovery stations that allow direct access to the storage medium. One significant advantage of hardware-based tools is their ability to work independently of the operating system, providing direct communication with the drive to bypass software-level restrictions or damages. This makes them highly effective for recovering data from severely damaged or failing drives. However, the drawbacks include the high cost of these devices and the need for technical expertise to operate them correctly. They are often used by professionals in data recovery labs, where controlled environments like cleanrooms are available to ensure the delicate handling of damaged components. For individual users or small businesses, the investment in hardware-based tools may be prohibitive, making them less accessible for everyday data recovery needs.
Specialized forensic tools represent another category of The Data Recovery Guide, tailored specifically for investigative and legal purposes. These tools are designed not only to recover data but also to preserve the integrity and authenticity of evidence for use in court. Forensic tools often include advanced capabilities such as recovering deleted files, analyzing hidden or encrypted data, and creating detailed reports that document the recovery process. The primary advantage of forensic tools is their ability to handle complex data structures and maintain a clear chain of custody, making them invaluable in legal investigations. However, they come with significant cons, including their steep learning curve and the need for specialized training to use effectively. Additionally, these tools can be expensive, with costs often justified only in professional forensic contexts. Despite their advanced capabilities, forensic tools may still struggle with severe physical damage, where hardware interventions are required before software can be effectively used. Balancing the pros and cons of different data recovery tools is essential, as the right choice depends on the specific data loss scenario, the level of damage, and the required expertise for successful recovery.

